Comparing Recuperative and Regenerative Burners for Industrial Needs
In the realm of industrial heating and energy conservation, selecting the most suitable burner technology is paramount. Burners play a critical role in numerous industrial processes, and their efficiency directly impacts an operation’s bottom line and environmental footprint. This blog post delves into a comparison of recuperative vs. regenerative burners, exploring their benefits and guiding you towards the ideal choice for your specific industrial needs.
Understanding Burner Technologies
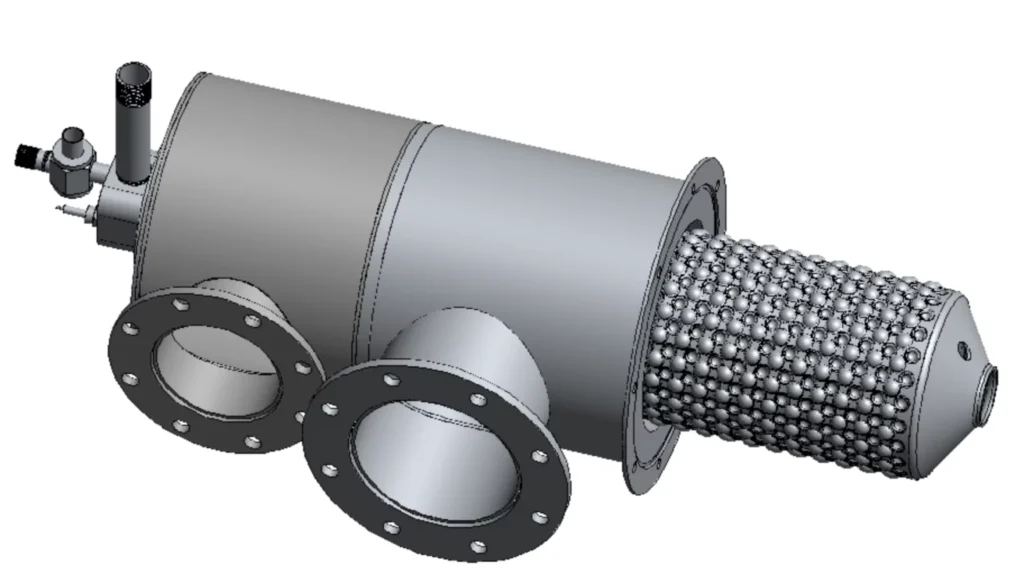



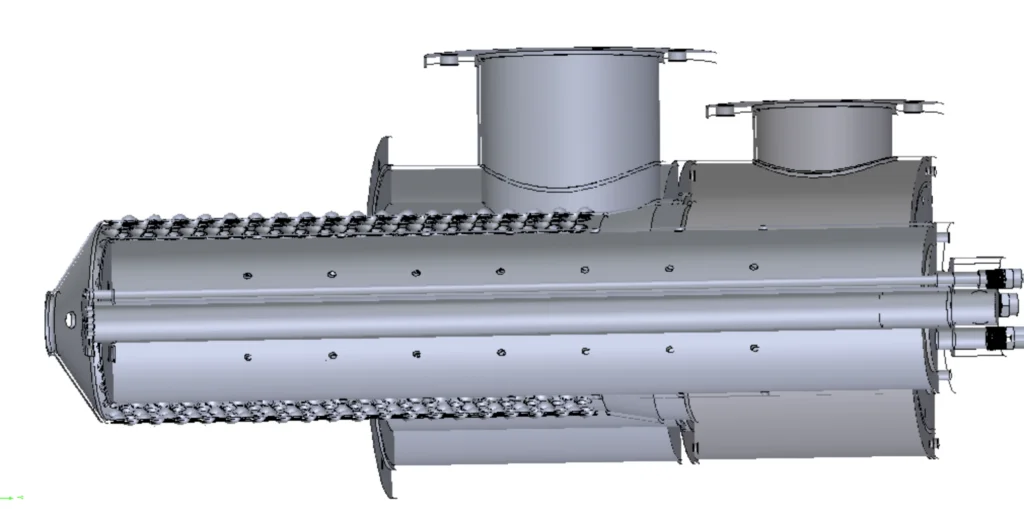

Recuperative Burners
- Definition: Recuperative burners preheat incoming combustion air by capturing waste heat from exhaust gases. This preheated air enhances fuel efficiency and reduces energy consumption.
- How They Work: Recuperative burners employ a heat exchanger positioned within the exhaust flue. Exhaust gases leaving the furnace transfer their thermal energy to the heat exchanger, warming the incoming air stream. This preheated air then mixes with fuel, resulting in a more efficient combustion process.
- Applications: Recuperative burners are often used in industries where moderate heat recovery is sufficient and initial cost savings are crucial, such as in small to medium-sized industrial furnaces.


Regenerative Burners
- Definition: Regenerative burners take heat recovery to another level. They utilize a cyclical valve system to alternately store heat in a regenerative media and transfer it to the incoming air stream.
- How They Work: Regenerative burners incorporate a rotating valve system with chambers containing ceramic regenerative media. During one cycle, hot exhaust gases pass through the media, heating it up. In the subsequent cycle, the valve redirects the airflow, forcing it through the hot media, and preheating the air before it enters the combustion chamber.
- Applications: Regenerative burners are ideal for high-temperature industrial processes that demand maximum energy efficiency and heat recovery, such as in steel manufacturing and glass production.
Key Differences Between Recuperative and Regenerative Burners
- Energy Efficiency: Both burner types promote energy efficiency, but regenerative burners achieve a higher degree of heat recovery, leading to greater fuel savings. Studies have shown that regenerative burners can recover up to 90% of the heat from exhaust gases, compared to 60-70% for recuperative burners.
- Heat Recovery: Recuperative burners boast a simpler design for heat recovery, while regenerative burners offer superior heat recovery capabilities due to the cyclical nature of their operation.
- Emission Reduction: Both recuperative and regenerative burners contribute to emission reduction by optimizing fuel combustion, thereby minimizing pollutants released during the process. However, regenerative burners are particularly effective in reducing NOx emissions due to their high-efficiency combustion process.
- Cost Considerations: Recuperative burners generally have a lower initial cost. However, regenerative burners can offer significant long-term savings due to their exceptional fuel efficiency and reduced operational costs over time.
- Maintenance Requirements: Regenerative burners, with their complex valve systems and regenerative media, typically require more extensive maintenance compared to recuperative burners. This complexity can lead to higher maintenance costs and downtime.
Benefits of Recuperative Burners
- Enhanced Efficiency: Recuperative burners preheat combustion air, leading to a more efficient burning process and reduced energy consumption.
- Reduced Emissions: By optimizing fuel combustion, recuperative burners help minimize pollutant emissions, contributing to a cleaner environment.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Recuperative burners offer a balance between upfront costs and operational savings, making them a suitable choice for various industrial applications.
Benefits of Regenerative Burners
- Superior Heat Recovery: Regenerative burners excel in heat recovery, achieving much higher thermal efficiencies compared to recuperative burners. This translates to significant fuel cost savings.
- Lower Fuel Consumption:Due to their exceptional heat recovery capabilities, regenerative burners necessitate less fuel to achieve the desired process temperatures.
- Extended Lifespan: The robust design and high-quality materials employed in regenerative burners often contribute to a longer lifespan compared to recuperative burners.
Choosing the Right Burner for Your Industry
Selecting the most suitable burner hinges on several factors specific to your industry:
- Industry-Specific Needs: Evaluate the typical operating temperatures required within your industry. Consider factors like production processes and desired heating rates. For example, the glass industry often prefers regenerative burners due to their high-efficiency heat recovery.
- Performance Goals:Identify your key performance objectives. If maximizing fuel efficiency is paramount, regenerative burners might be ideal. Conversely, if upfront cost is a primary concern, recuperative burners could be a viable option.
- Environmental Impact: Factor in environmental regulations and your commitment to sustainability. Both burner types contribute to emission reduction, but regenerative burners offer superior efficiency, making them more suitable for industries with stringent environmental standards.
Conclusion
By understanding the distinctions between recuperative vs. regenerative burners, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your specific industrial needs. Whether prioritizing cost-effectiveness, environmental impact, or exceptional fuel efficiency, ENCON Thermal Engineers can assist you in selecting the optimal burner technology for your operation. Contact us today for a consultation or to explore our comprehensive range of burner solutions.








